LET US EVALUATE YOUR CASE
Dr. de Quintana will make an accurate diagnosis and explain the options to restore your quality of life.
+34 699 922 118 info@drdequintana.com location
BRAIN SURGERY
Brain disease, or brain pathologies, is a subspeciality of neurosurgery that requires experience and advanced technology to successfully treat.
In this field, Dr. de Quintana has been the Coordinator of Neuro-Onology for more than 15 years at a pioneering hospital in brain disease: Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau.
This section shows different brain conditions as well as the most innovative techniques used.
PATHOLOGIES
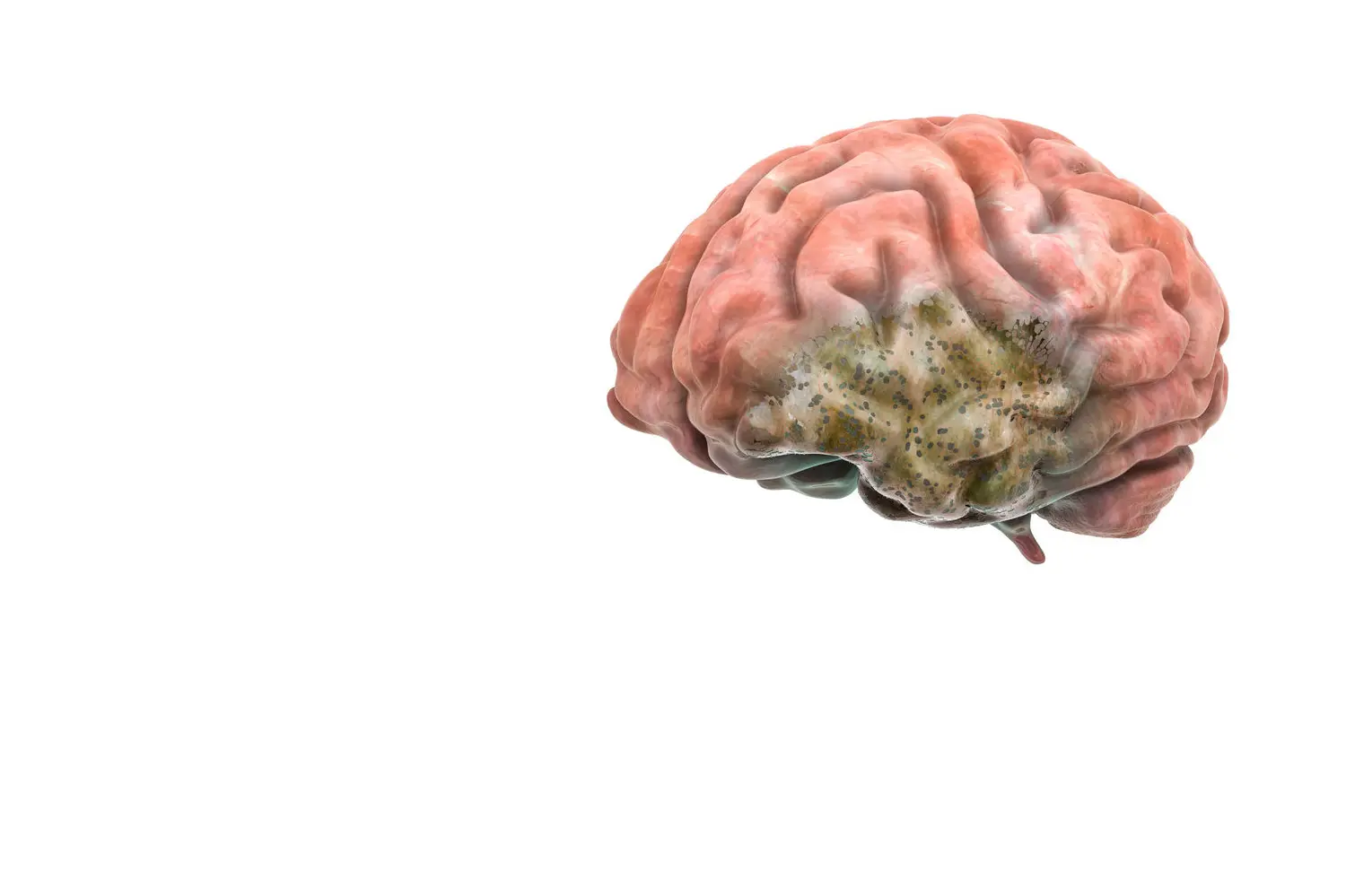
INTRA-AXIAL BRAIN TUMORS
GLIOMAS AND METASTASES
The two most frequent tumors of this type in the brain are Gliomas (tumors of brain itself) and Metastases (the origin of the tumor is in another organ; for example, the lungs).
The objective of neuro-oncology surgery is to remove all the tumor without creating neurological deficits (maintain patient safety). To achieve this objective, it is important to be at the forefront of the latest technology and scientific knowledge.
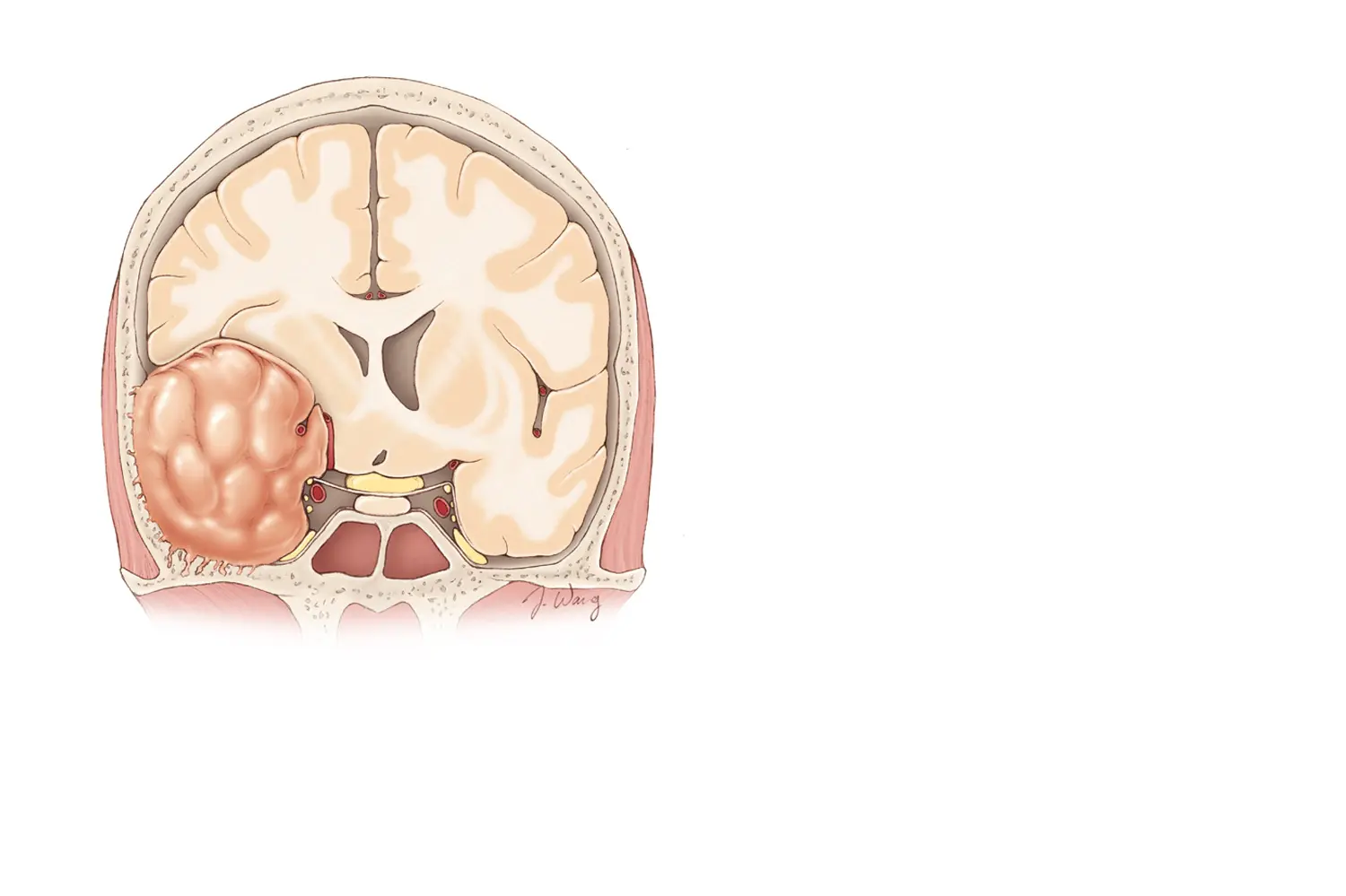
EXTRA-AXIAL BRAIN TUMORS
BRAIN TUMORS
The location of the tumor is not in the brain itself, it is in the space between the brain and skull bone. Although its location is not in the brain, it can compress the brain and create neurological symptoms.
One of the most important considerations is the exact location of the tumor, because this can significantly change the approach. Once again, these tumors require extensive experience in this field to obtain the best outcomes.
The most frequent tumors of this type are: Meningiomas, Neurinomas, and Pituitary Adenomas.
HYDROCEPHALY
EXCESS OF CEREBROSPINAL FLUID
Hydrocephaly occurs when there is an excess of fluid (cerebrospinal fluid) on the brain. It can occur for two reasons:
1- Excess production.
2- Absorption deficit.
This type of illness requires experience to diagnose, yet if necessary, the surgical solution is technically simple.
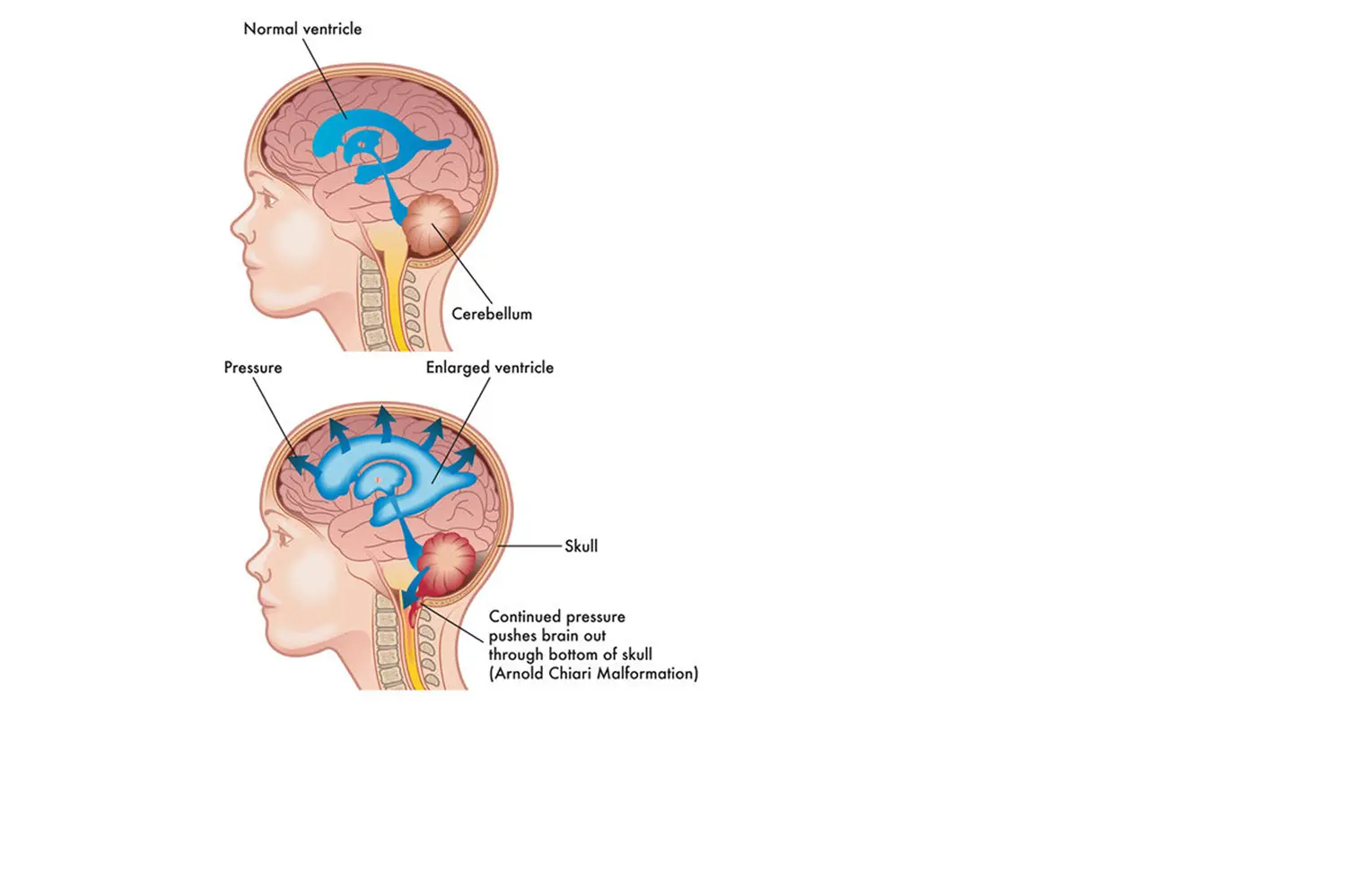
CRANIOSPINAL MALFORMATIONS
ARNOLD-CHIARI MALFORMATION
Produced by a bone malformation between the union of the skull and the spine that causes the compression of nerve tissues.
This is a type of alteration that requires a precise diagnosis in order to offer the best solution or therapeutic alternative.
COMPRESSION OF CRANIAL NERVES
TRIGEMINAL NEURALGIA
This is a group of diseases that can be very limiting and painful, and can significantly impact quality of life.
While most cases are resolved with pharmaceutical treatment, sometimes they require some neurosurgical alternative to improve or eliminate pain.
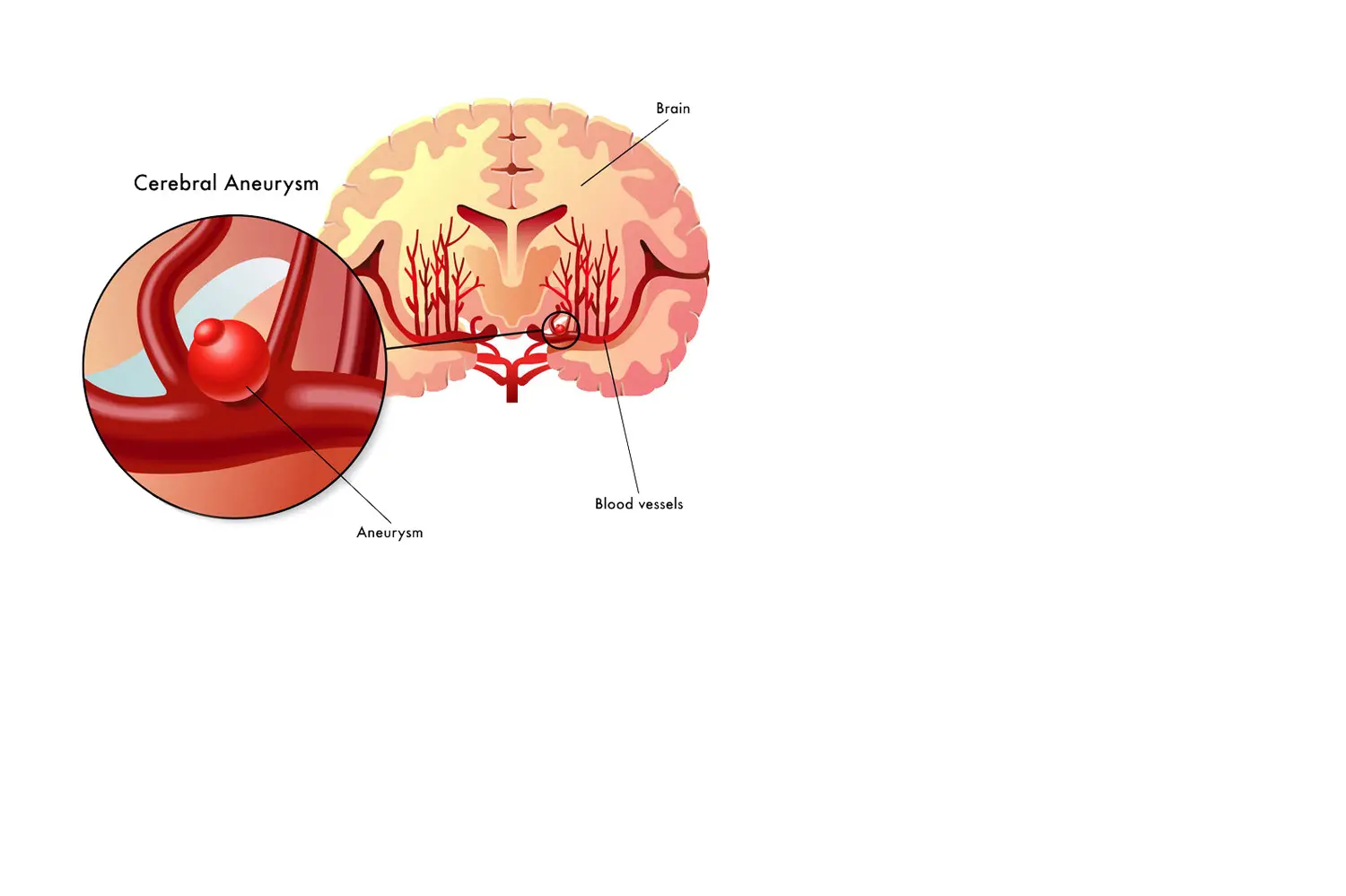
VASCULAR DISEASE OF THE BRAIN
VASCULAR MALFORMATIONS OF THE BRAIN
In this group we include:
- Cerebral aneurysms.
- Cerebral malformations.
- Cavernomas.
In this type of pathology, a multidisciplinary team is essential, where the Neurosurgeon works together with Neurologists and Interventional Neuroradiologists.
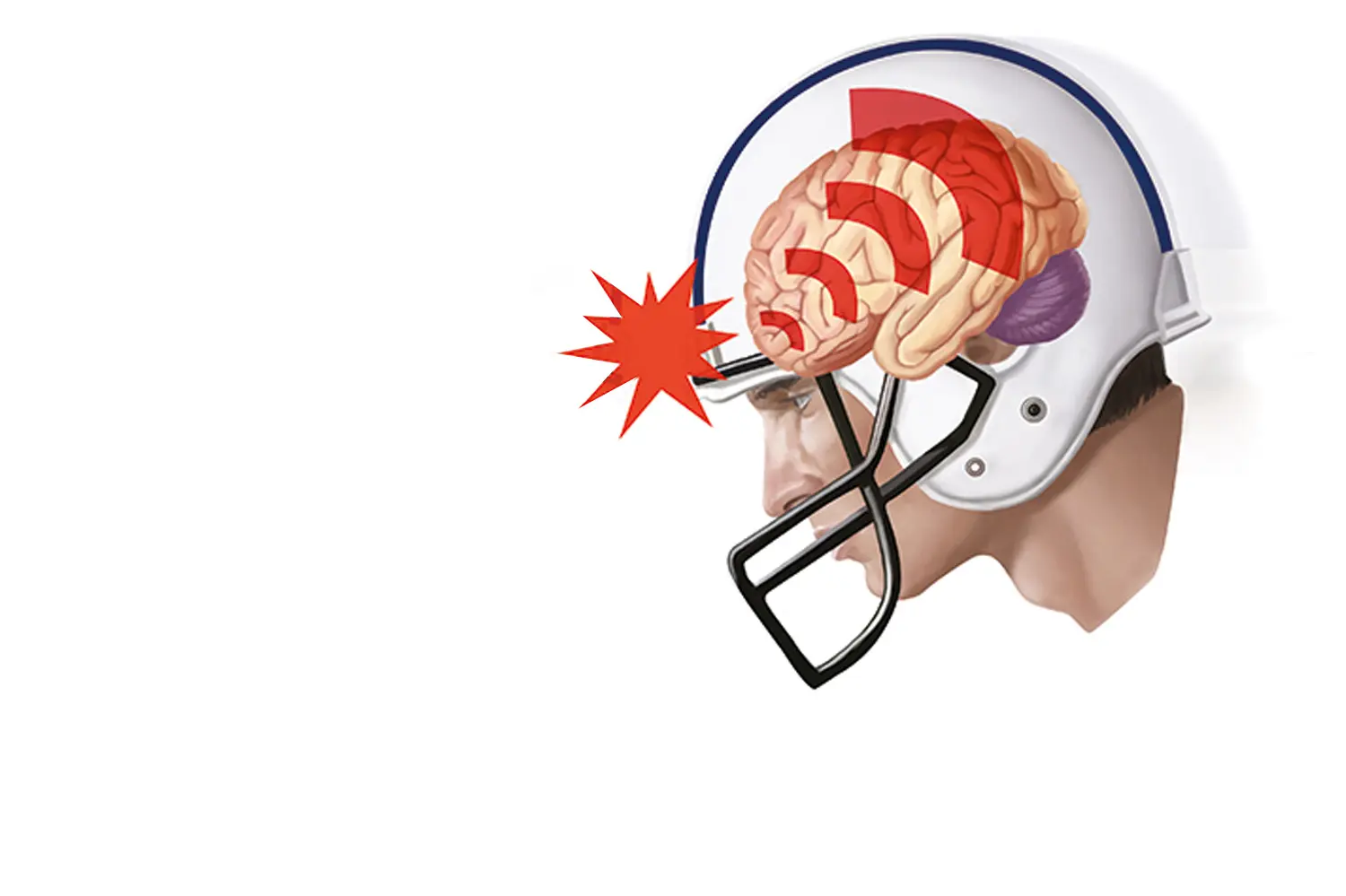

HEAD INJURIES
INJURIES CAUSED BY IMPACT
Injuries produced by an impact (accident) and that can cause different types of brain conditions. There are two major periods that require special attention:
- Phase 1 (Acute): there is teamwork between Neurosurgeons and Intensive Care Physicians (ICU) to offer the best therapeutic management and stabilize the patient.
- Phase 2 (Reconstructive): offer all the therapeutic alternatives that we have, to minimize or eliminate the sequelae (lasting effects) of the trauma.
INNOVATION


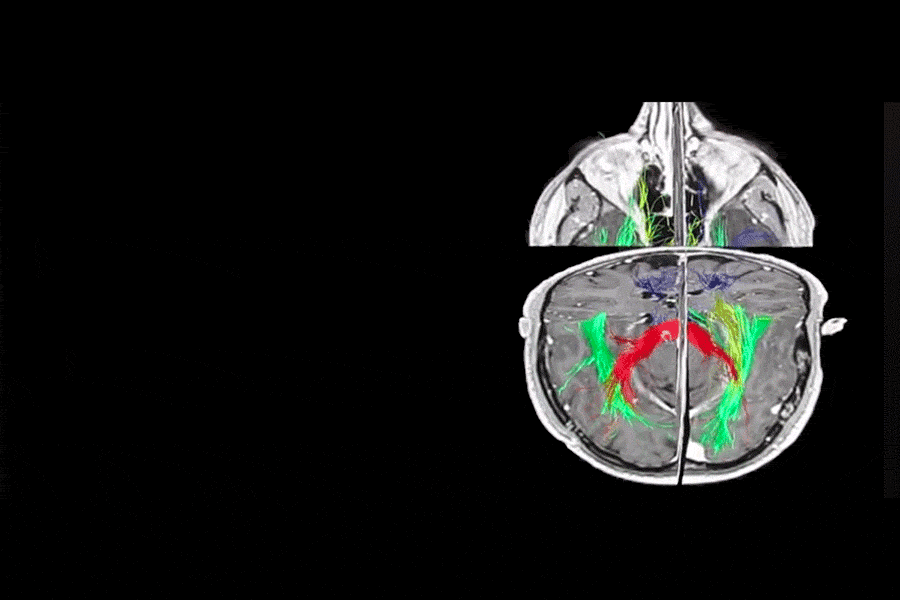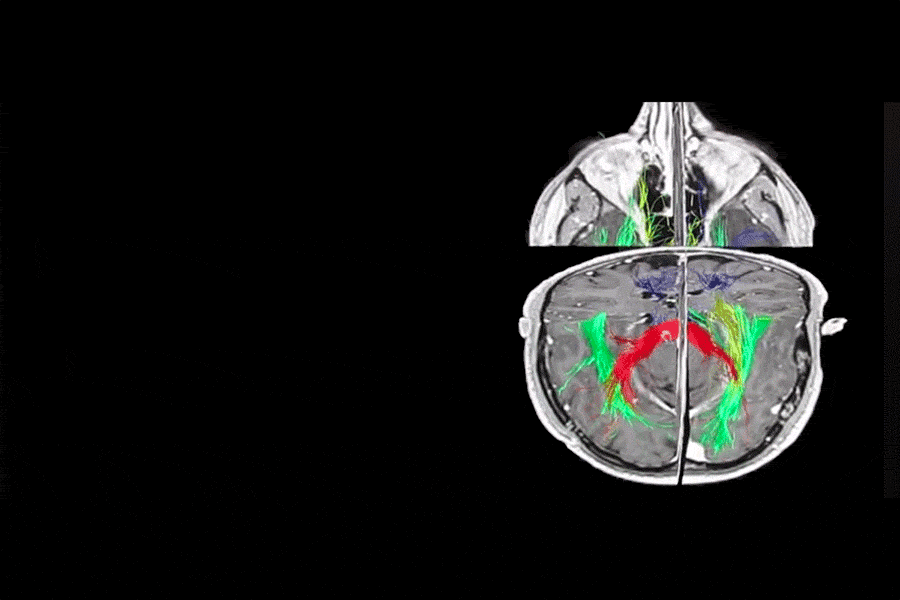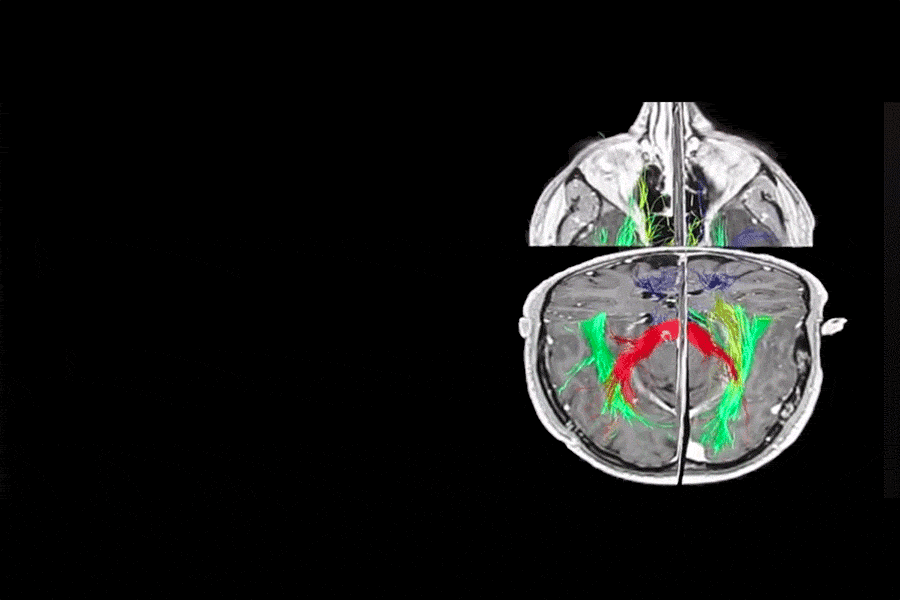
3D PLANNING AND TRACTOGRAPHY (DTI)
SURGICAL PLANNING
One of the most important aspects when it comes to brain surgery is excellent surgical planning. This allows us to anticipate what will happen during surgery and offer a safer surgery for the patient. In this field there have been many advances thanks to 3D Planning and the possibility of performing Tractography (DTI). Tractography allows us to see the neural pathways and their relationship with the tumor, as can be seen in the video (Blue = Motor pathway, Green = Language, Yellow = Visual pathway, and Red = Corpus Callosum).
Recently, Dr. de Quintana's team published an article on the benefits of tractography in brain surgery in the world-renowned journal, World of Neurosurgery.
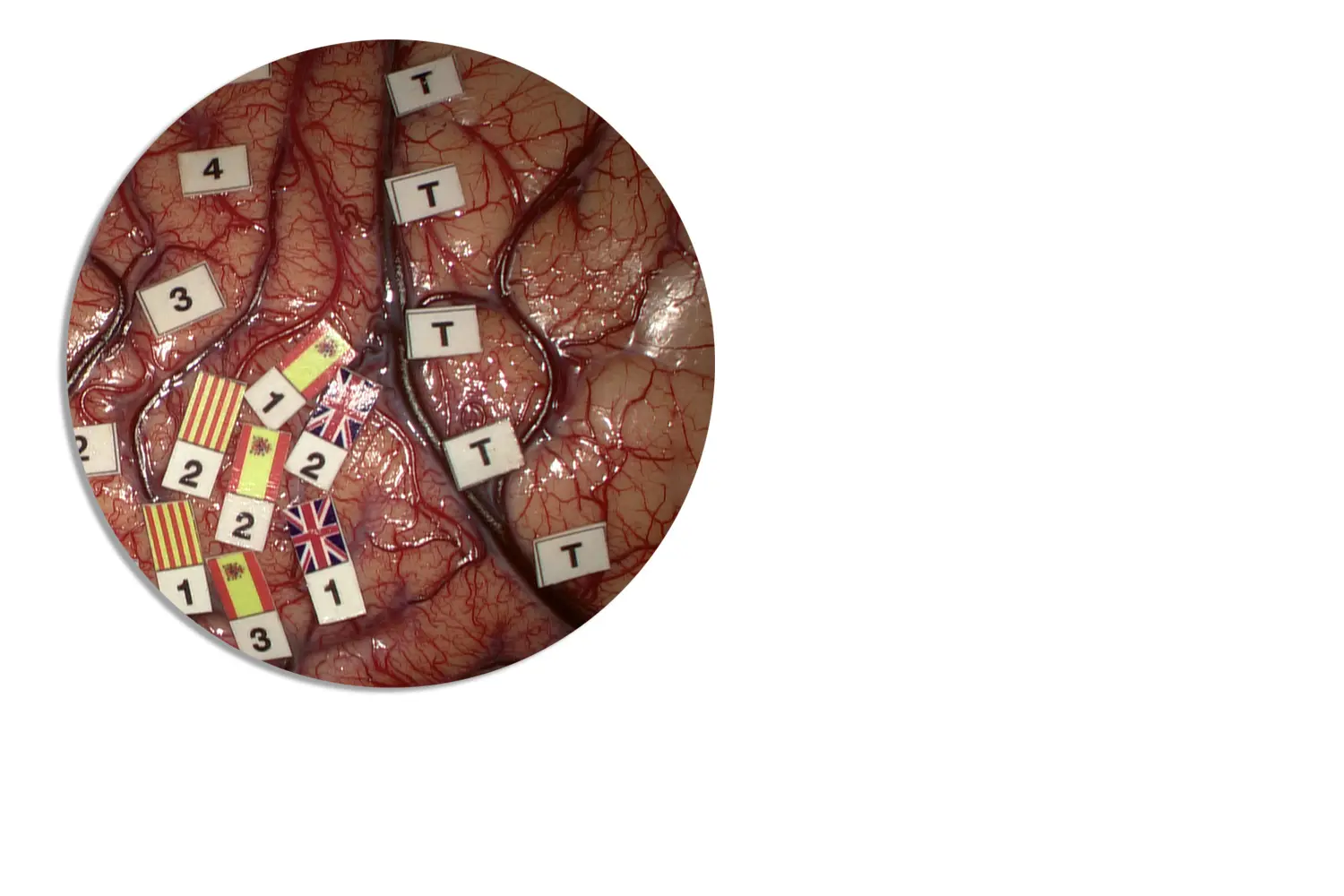
BRAIN MAPPING
AWAKE SURGERY
During surgery, and with the help of pre-operative planning, we must locate the different functional areas of the brain (Motor, Sensory, Language, and Visual) to preserve them and be able to safely remove the tumor. This is achieved through intraoperative neurophysiology (Mapping) and requires vast experience for its interpretation.
Due to its complexity, the language area is the most complicated area to monitor. Sometimes the patient is required to be awake during surgery to have more control over this functional area.
Dr. de Quintana not only has extensive experience in this field, but is also a pioneer in monitoring the different languages spoken by the patient, as can be seen in the illustration. The location of each language the patient speaks is represented by a different flag (cortical representation).


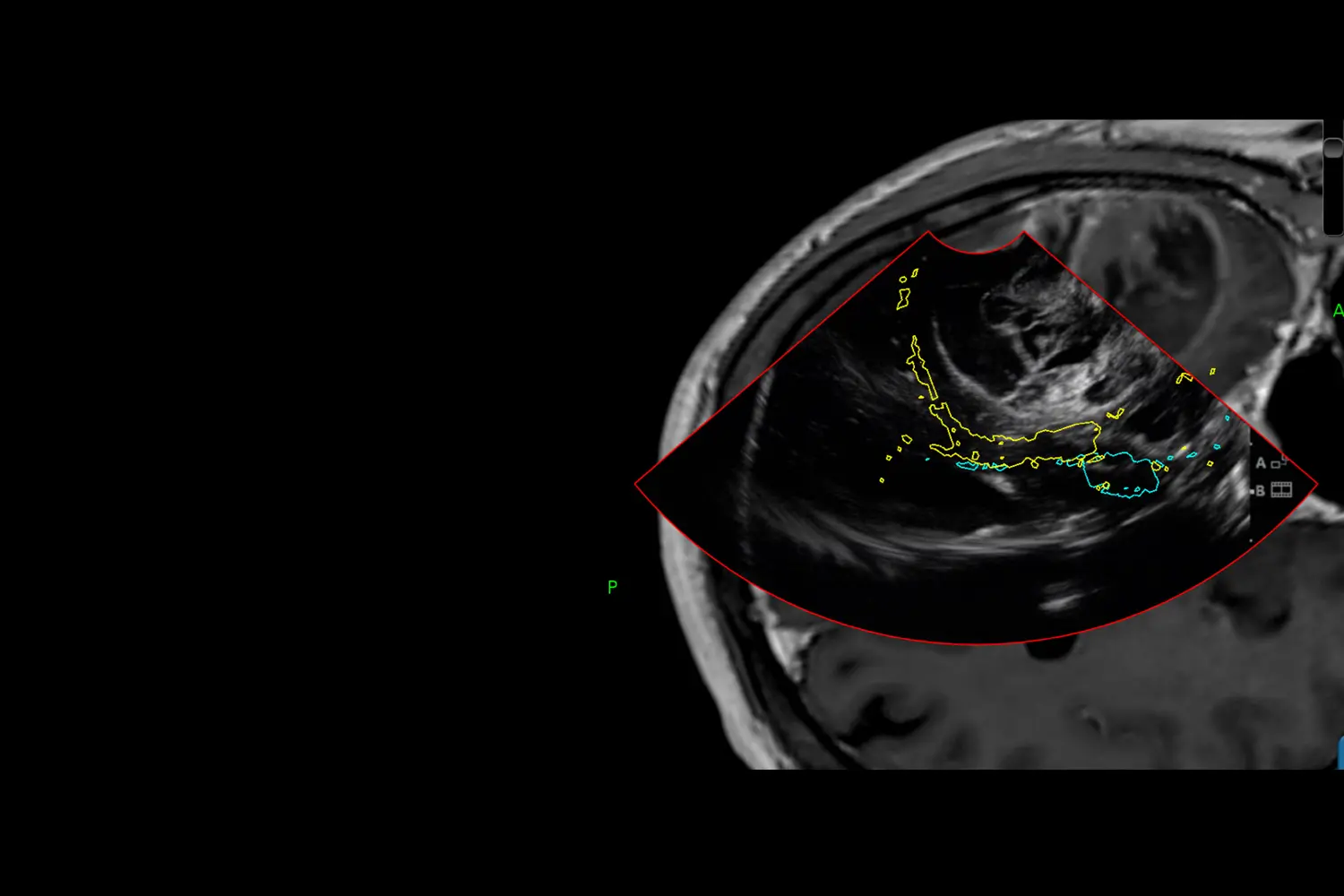
NAVIGATED BRAIN ULTRASOUND
IMAGE CONTROL
During the resection of the tumor it is very important to have control with imaging to be able to objectively determine whether there has been a complete resection (excision) of the mass. This can be achieved through navigated ultrasound, which is an image that guides us in real time and can be performed as many times as necessary until we achieve our goal.
This is a technique that requires a lot of experience to correctly interpret the images, and for this reason, Dr. de Quintana leads courses to guide other neurosurgeons in its use: ultrasoundneurosurgery.com
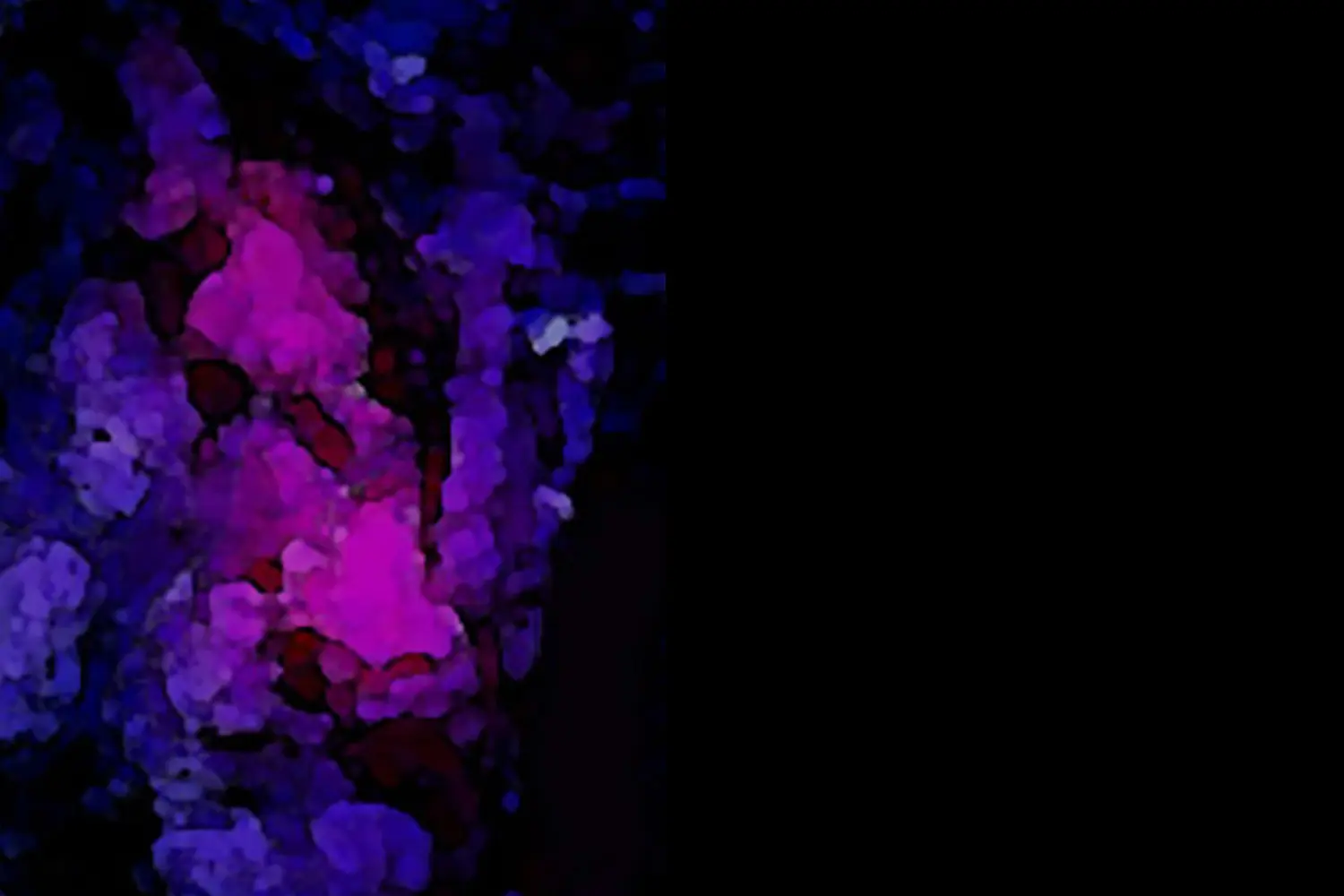



FLUORESCENCE
5-ALA
5-ALA is a dye that is used to highlight and delineate high-grade gliomas from normal brain tissue. It is complementary to ultrasound and allows us to verify during surgery that the entire tumor has been removed.
In this example video, you can see how under normal lighting the tumor does not stand out. However, under fluorescent lighting it clearly shines, which indicates that it is a tumor (pink).
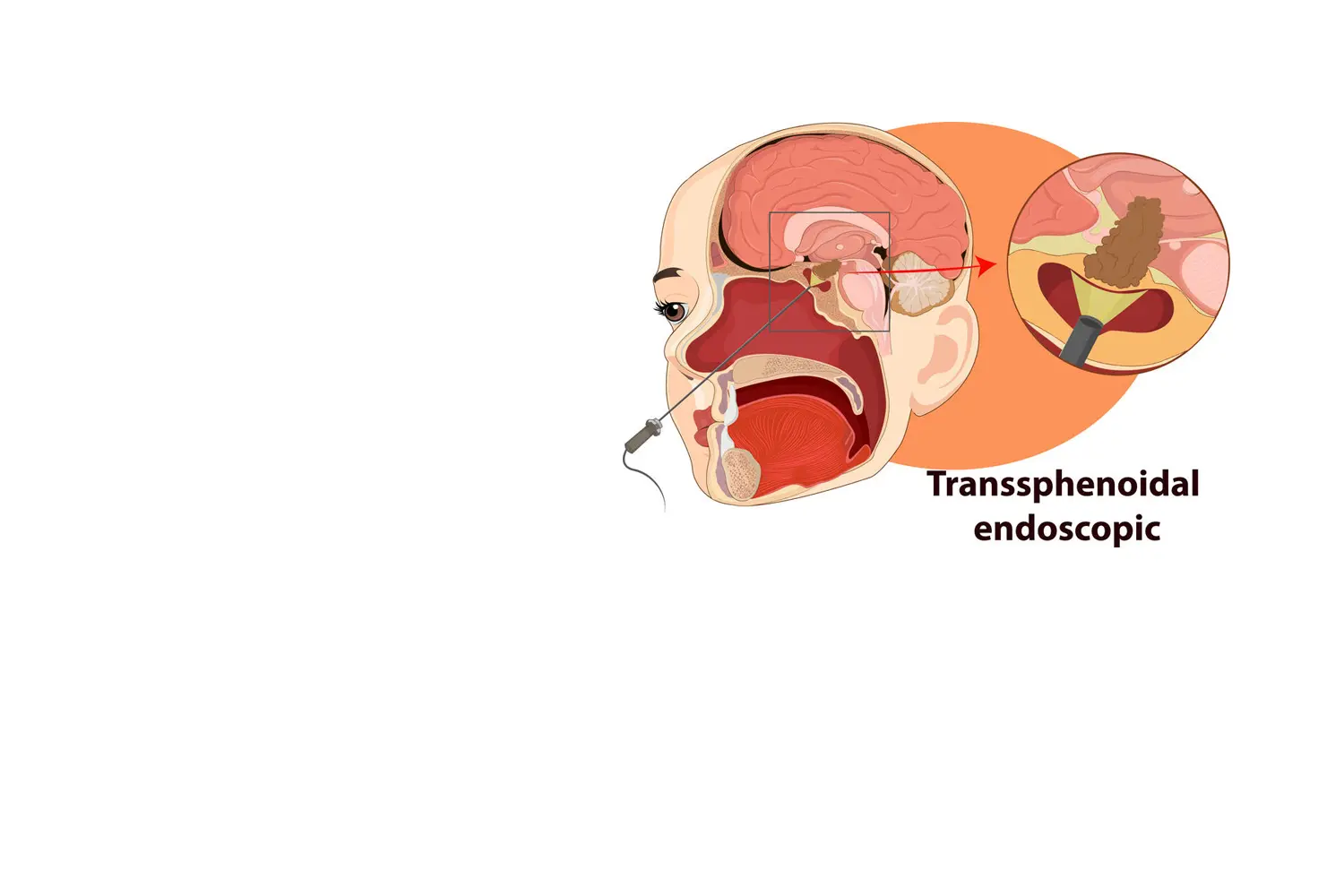
BRAIN ENDOSCOPY
BETTER VISUALIZATION OF THE TUMOR
One of the great advances in skull base surgery has been the introduction of endoscopy to achieve better visualization of the tumor and its relationship with brain structures as well as performing a less invasive and safer surgery.
A classic example is removing a tumor through the nose, the most common example being pituitary surgeries, but endoscopy can also be useful for other approaches such as to the skull base.
OTHER TECHNIQUES
- Neuronavigation (brain GPS).
- Stereotaxic surgery.
- Brain microsurgery.
- Neuro-endoscopy as a treatment for hydrocephalus.
- 3D reconstruction of a cranial defect.
- Minimally invasive techniques for facial pain.
- Surgical technique to avoid bleeding in brain biopsies.
FAQ´S
- Write down all your questions or concerns in a list. Our job is not only to operate, but to respond to any questions you may have. When you are nervous about the consultation, it is easy to forget what you want to ask. So, if it is written down, this makes it easier.
- One step at a time. The process takes time and it is important to take it one step at a time to make the process less stressful. Our responsibility is to guide you in this process and help you through it.




- Be strict with taking your medication as prescribed.
- Clean and care for the wound.
- Rest. For the first month after surgery we recommend taking it easy and avoiding any type of stress or strain.
- Attend the outpatient visits with your Neurosurgeon to complete postoperative follow-up. Also, in the case of a brain tumor, the outpatient visits are crucial for discussing results of the biopsy (knowing the exact diagnosis of the tumor and its genetic characteristics) and evaluate whether or not a complementary treatment to the surgery is necessary.


1- Immediate postoperative complications (Uncommon, but potentially dangerous) such as:
- Problems with the cerebral blood vessels - a vessel can break and cause bleeding or it can become obstructed and leave an area without blood flow (ischemia).
- Brain edema.
- Epileptic seizures.
2- Secondary complications (More frequent, but potentially less dangerous) such as:
- Problems with wound closure.
- Infection - which can be superficial or deep.
- Fistula of cerebrospinal fluid.

LET US EVALUATE YOUR CASE
Dr. de Quintana will make an accurate diagnosis and explain the options to restore your quality of life.
+34 933 800 999 info@drdequintana.com location